Tylosis
Esophageal carcinoma is associated with a TEC mutation (Tylosis with Esophageal Carcinoma). Tylosis is the thickening (hyperkeratosis) of the palms and soles of the foot. There is 50 to 90% risk of developing esophageal carcinoma in patients with tylosis after the age of 70 years.
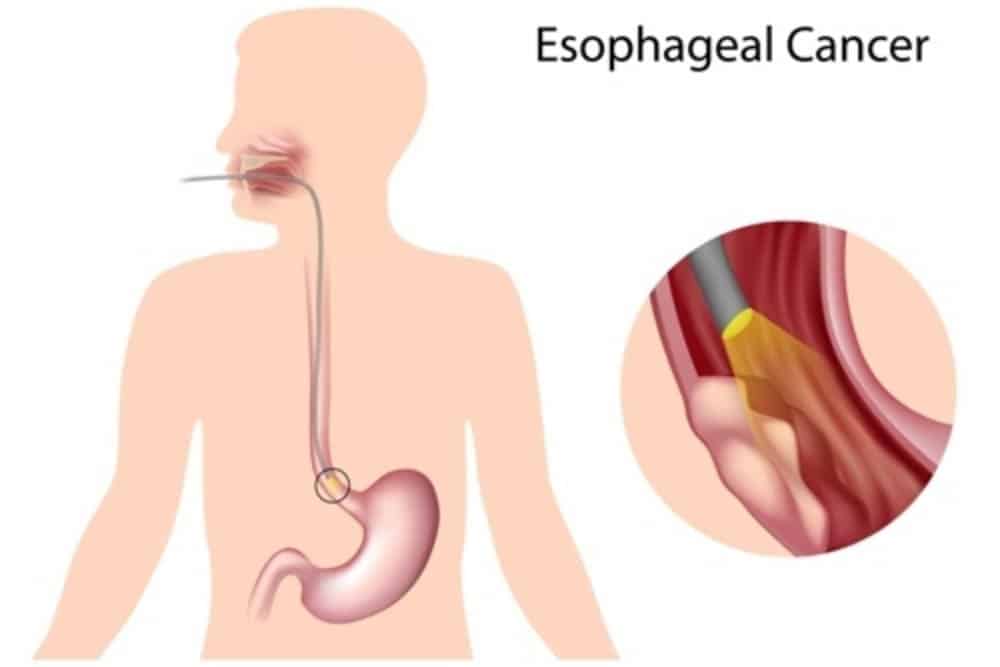
Diagnosis of esophageal cancer is done through a barium swallow, and then endoscopy of the upper gastrointestinal tract to see the tumor and take a biopsy sample. Through biopsies, doctors investigate the form and behavior of cells in the esophagus. Other exams include bronchoscopy to evaluate the extension of the tumor into the bronchi, and CT scan combined with positron emission tomography (CT-PET).
After the diagnosis, staging of tumor is done by the TNMG (tumor size, lymph node involved, metastasis and histological grading) classification. Treatment is initiated by radiotherapy, which is treatment of choice for the upper two thirds of the esophagus, while tumors of the lower one third of the esophagus are usually treated by a surgical approach. After treatment, the survival rate is around 10% for 5 years. However, if radiotherapy is combined with chemotherapy, the survival rate is increases up to 25% for 5 years. Palliative care for advanced disease incudes analgesia, nutritional support by alternative food channel such as a bypass operation, esophageal intubation (tube feeding), or permanent jejunostomy (jejunum connection with the outside).

