Prostate glands and seminal vesicles are the parts of the male reproductive system and lie in the pelvis. Prostate cancer is the type of cancer in which there is the development of cancerous cells in the prostate gland – a small gland surrounded by anus, intestines, and urinary bladder. Prostate cancer is very prevalent in men all over the world and is one of those cancers that mostly results in the death of the patient. The prostate gland weighs about one ounce, and the shape of the gland is almost similar to a walnut. The seminal vesicles are the smaller glands, and each prostate gland has one of these seminal vesicles connected to it.
The prostate gland lies below the bladder and is present around the urethra surrounding the urethra tube. When the cancer cells in prostate glands develop and start causing inflammation, then patient starts having a problem urinating correctly. Prostate glands play an essential role in the fertility of a male as it makes a lubricating fluid for the sperms to bathe in. However, in a male having prostate cancer, the chances of fertilization decrease due to less lubrication of sperms in the semen. Prostate cancer progresses in the body due to the breakdown of a prostate tumor, which spreads the cancer cells to blood vessels and lymph nodes.
Prostate cancer cells start spreading the cancer cells to the normal tissues and blood vessels attached to other healthy organs, causing the progression of cancer in the whole body. Prostate cancer cells can affect other healthy organs by connecting to healthy tissues and forming tumors there. In advanced stages, it might spread to bones, liver, lungs, and kidney. The spreading of prostate cancer cells in other healthy body tissues is another disorder known as metastatic prostate cancer.
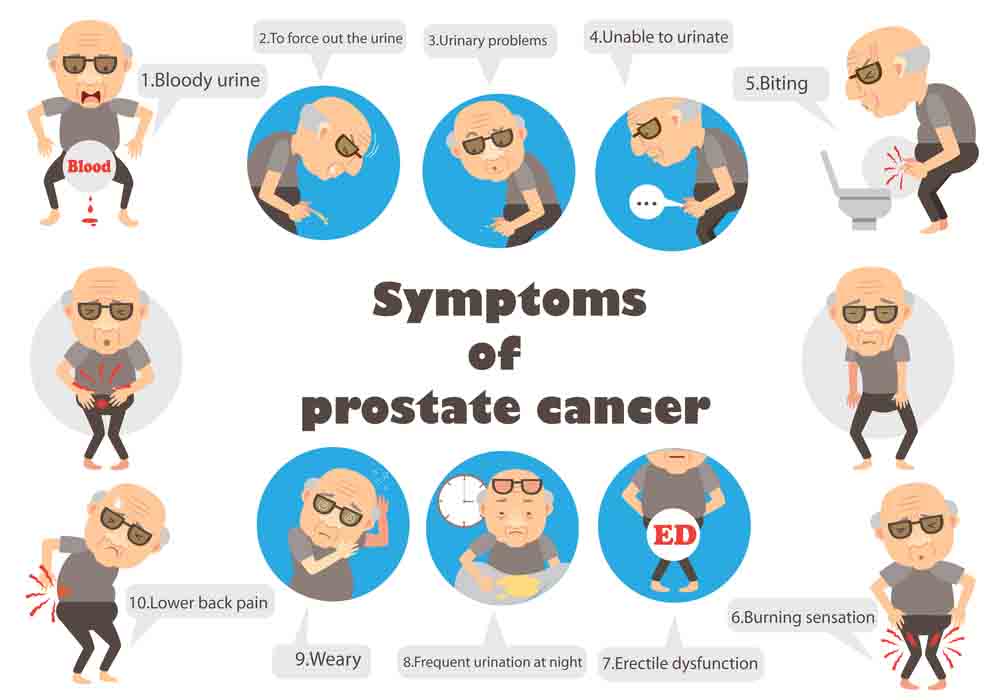
Symptoms of prostate cancer
The growth of carcinogenic cells in the prostate glands can be either benign or malignant. The type of tumor growth in which the cancerous cells do not spread to other parts of the body is known as benign. The type of cancer the benign cell growth causes is known as benign prostatic hyperplasia or BPH, and it is usually not life-threatening for the patient. The benign growth does not damage the surrounding tissues of the prostate gland, and the surgical removal of this type of benign tumor is also very successful.
The other type of cancerous cell growth is known as malignant, which is quite dreadful and sometimes become fatal for the patient. The malignant prostate cancer spreads actively in the tissues and organs surrounding the prostate gland and mostly in the rectum or bladder. The malignant type of prostate cancer also targets and spreads to the other body parts like bones or lymph nodes. Unfortunately, malignant cancer grows back again even after the surgical removal of cancer.
In the earlier stages of prostate cancer, there are no obvious signs and symptoms of the disease. But with the progression of cancer in the glands, some specific symptoms appear that are clear indications of prostate cancer like enlargement of the prostate gland. However, most of the males complaining about the problems regarding urination and the urinary system might have prostate cancer. Following are the symptoms of prostate cancer:

