Diagnosis
A person may be supposed to have leukemia if he experiences some of the concerning symptoms or risk factors. To make a definitive diagnosis – doctors start with taking the history and then do a physical examination of the person. But physical examination may not be enough to diagnose the disease – doctors will use imaging tests, biopsies or blood tests in most of the cases.
Tests
To diagnose CLL, many tests are used.
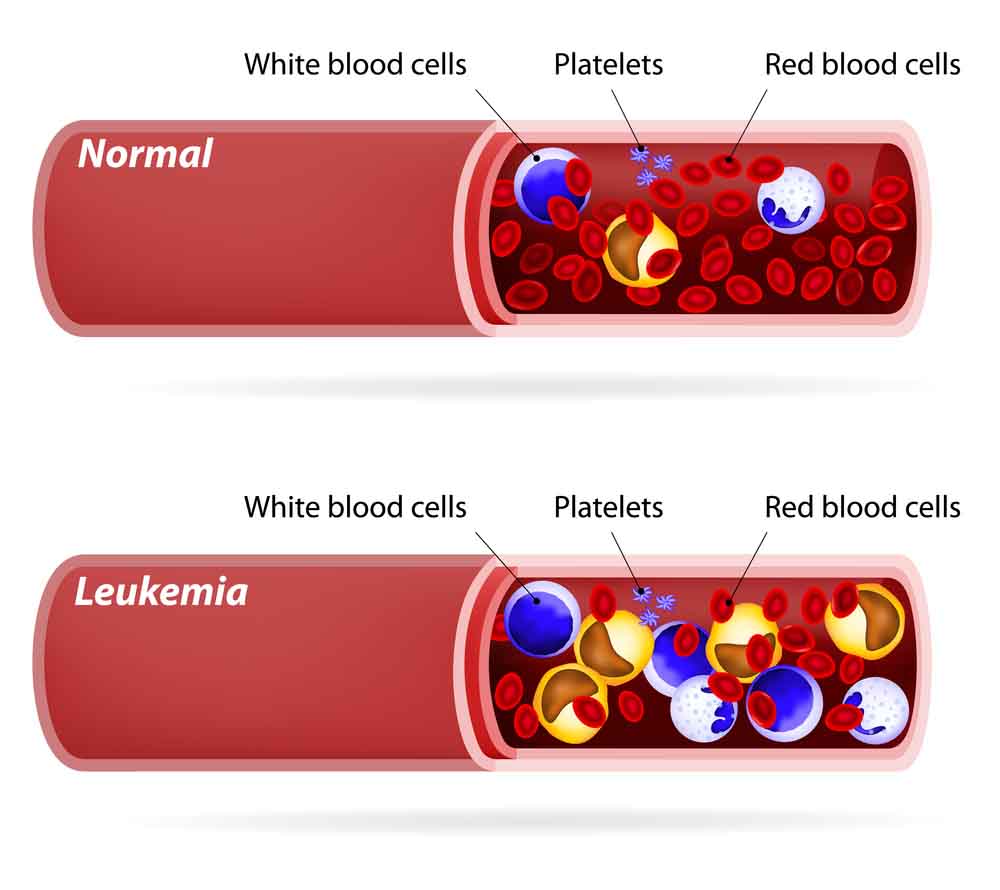
Complete Blood Count determines the total amount of Red blood cells, white blood cells, and leukocytes. To determine if the cells are abnormal in shape or appearance, blood is examined under the microscope.
To find out the sign of CLL, tissue biopsies are taken from lymph nodes or bone marrow. No matter these samples are small in size, but this is a very important test to identify the speed of production of cells and the type of leukemia. To check the growth of cancer to other organs, biopsies of spleen or liver are also taken.
Staging
Staging is done after the diagnosis of leukemia. Different types of leukemia are staged on a different basis. To stage the CLL, the blood and bone marrow is checked for the presence of immature WBCs or myeloblasts and the number of white blood cells at the time of diagnosis.
The type of cells involved in the disease and appearance of cancerous cells under the microscope is checked to stage the CLL.
Assessing the development
There are many other tests used to check the development of the disease. To check if cancerous cells are attacking or affecting the liver, test for assessing the liverfunction is used. To determine the growth rate of the cancerous cells, the DNA of the cells is examined by flow cytometry.
X-rays, CT scans, ultrasounds, and other imaging tests are used to check for damage to other body organs by cancerous cells. The lumbar puncture technique is used to check if the cancer is spreading to the Central Nervous System (CNS). This technique involves the insertion of a sterile needle between the vertebrae of the lower back and spinal fluid is collected and tested.

