Infectious mononucleosis is also known by the popular name kissing disease, or mono. It is a contagious disease caused by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). It is an acute, self-limiting. EBV is one of the most common viruses worldwide. Infectious mononucleosis is characterized by symptoms such as a sore throat, prolonged fatigue and malaise, fever, lymphadenopathy, and lymphocytosis (an increase in number of lymphocytes, more specifically CD8+ T cells). It can also be described as a triad of fever, lymphadenopathy, and pharyngitis.
A very similar disease can also be caused by the cytomegalovirus, toxoplasma gondi, human herpes virus 6 and 7, and HIV type 1. However, all of these infections are not as common as EBV. This virus is a member of human herpesvirus family and is also known as herpes virus type 4.
Infectious mononucleosis caused by EBV has two forms, one is subclinical and asymptomatic, where the patient is only seropositive for the infection but shows no symptoms, also known as atypical infectious mononucleosis. The second form is a clinical syndrome in which the patient presents with the complete symptomatology, also known as typical infectious mononucleosis.
EBV spreads through the saliva, mucous, and air droplets. Contamination or transmission to a healthy person can be done by kissing or making direct contact with respiratory droplets, hence the name kissing disease. It also spreads through unprotected sexual contact because the virus is also present in the cervix. When an individual gets the infection, EBV multiplies in the B lymphocytes. B cells either undergo lysis or go polyclonal multiplication in the latent stage of the disease. The immune response against EBV is through CD8+ T cells and natural killer cells.
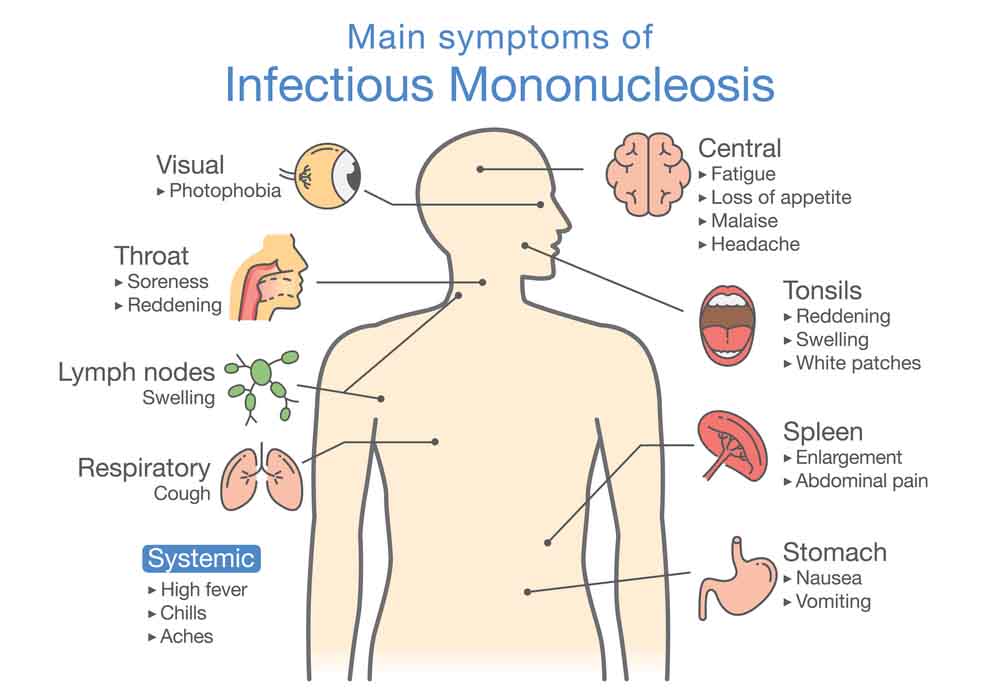
Histologically, infectious mononucleosis is associated with atypical lymphocytes and also giant cells derived from lymphocytes, known as Reed-Sternberg cells. The clinical features of infectious mononucleosis include the following signs and symptoms:
Symptoms of an atypical presentation
In the atypical presentation of mononucleosis, the patient may only display lymph node swellings without fever or any other symptoms. In other cases, they have a fever of unknown origin, which is not associated with lymph node swelling. In very rare cases, mononucleosis may mimic other viral infectious diseases, especially viral hepatitis. This presentation is more common in seniors.

